Percentage of Baby Boomers That Voted Before Age 35
Racial variety will be the about defining and impactful characteristic of the millennial generation. Newly released 2015 Demography data points to millennials' role in transitioning America to the "majority minority" nation information technology is becoming.
Millennials betwixt ages 18 and 34 are at present synonymous with America's young adults, fully occupying labor force and voting ages. They contain 23 percent of the total population, 30 percent of the voting historic period population, and 38 percent of the primary working age population. Among racial minorities their numbers are even more than imposing. Millennials make upward 27 percent of the total minority population, 38 per centum of voting historic period minorities, and a whopping 43 pct of primary working historic period minorities.
Millennial diversity stands out
More of import for the future is the clear disparity between the racial makeup of the millennial generation and of preceding generations. Millennials were born during a period of heightened immigration and more than modest white growth (See Figure 1).

Equally of 2015, the population 55-years-sometime and older, which includes virtually Baby Boomers, is "whiter" than the state equally a whole (75 percent vs. 61.half dozen percent) and, among them, blacks are the largest racial minority. Those in the 35- to 54-yr-old age grouping, including Gen Xers and the tail-stop of the Babe Boom generation (at 61.5 percent white, 17.vi percent Hispanic and 12.five percent black), roughly represent the national racial composition.
Plain, the millennial generation is ushering in the nation's broader racial diversity. Overall, millennials are 55.8 percentage white and most 30 percent "new minorities" (Hispanics, Asians and those identifying as two or more races). Back in 2000, when millennials were but beginning to bear on demographics, this young adult age grouping was 63 percentage white, whereas in 1990 information technology was 73 percent white.
Quite a few states showroom more diversity in their millennial populations than the national numbers prove (run across Map i). In California, less than i third of millennials are white, and more than lx percent are new minorities (run into Table one).
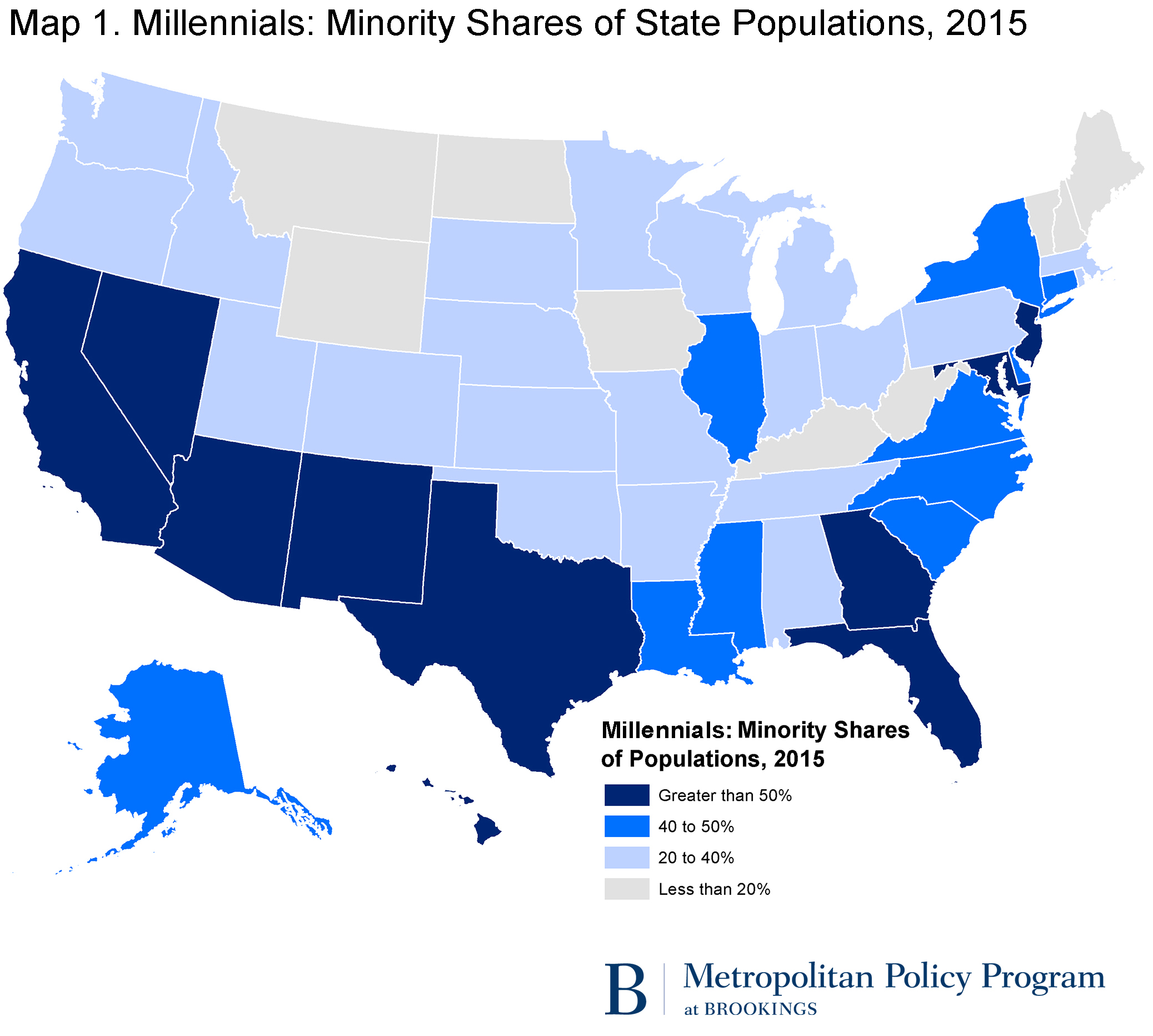
Minorities comprise more than than half of the millennial populations in 10 states, including Texas, Arizona, Florida, Georgia, and New Bailiwick of jersey. In 10 additional states, including New York, Illinois, Virginia, North and Due south Carolina, minorities comprise more than 40 percent of millennial residents. Other states accept whiter millennial populations, only only nine states are home to largely (over 80 percent) white millennial populations (e.g. Wyoming, Iowa, West Virginia, and Maine).
A span to the post-millennial generation
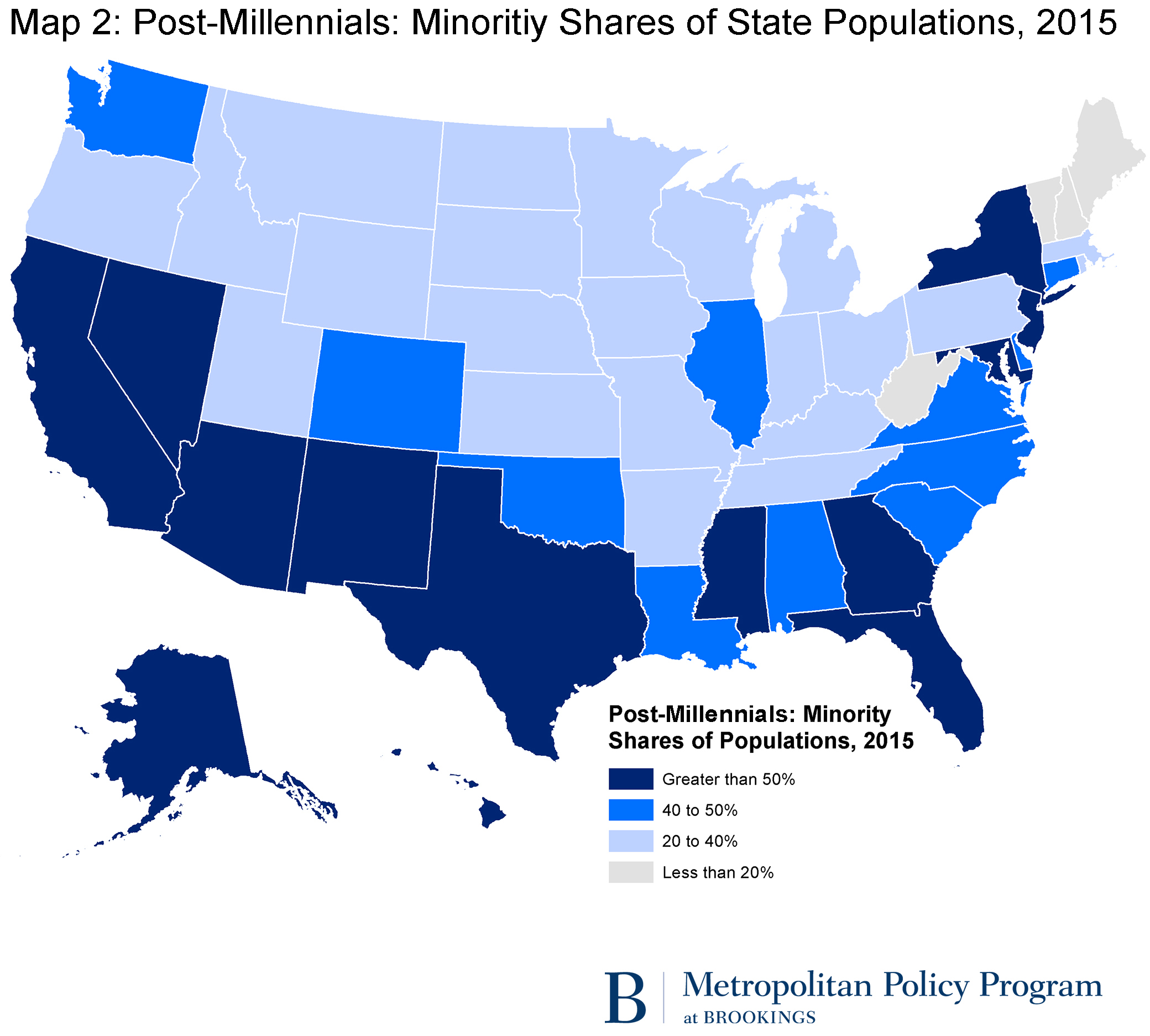
The idea that millennials are a bridge to a much more than diverse America is axiomatic from looking at the mail service-millennial generation—persons now under age 18. Whites comprise just over half (51.5 percent) of this generation. Of this subset, people betwixt ages one through 5 are minority white (see Effigy one). Nearly 34 percent of this group consists of new minorities, and almost a quarter is fabricated up of Hispanics.
A noteworthy demographic dynamic is making the immature mail-millennial generation more racially diverse – the absolute turn down in the number of white children (persons under age eighteen). This began to occur between 2000 and 2010, and continued betwixt 2010 and 2015. More white children are aging past 18 than are being born or immigrating. Although white fertility is low, information technology is the aging of the white population, with proportionately fewer women in their childbearing years, that is leading to a projected long term continuation of this trend. It is broad based, occurring in 46 states (see Tabular array 2). This means that the route for youth population gain in most states is through minority gains, via fertility or in-migration; thus making the kid population more racially diverse.
At present, 14 states house "bulk minority" child populations (see Map 2). In California, minorities comprise almost iii quarters of post-millennials; and in Texas it's ii thirds. Overall, 25 states business firm post-millennial populations that are more than 40 percent minority and in only four (New Hampshire, Maine, Westward Virginia, and Vermont) is this generation largely white.
The racial generation gap
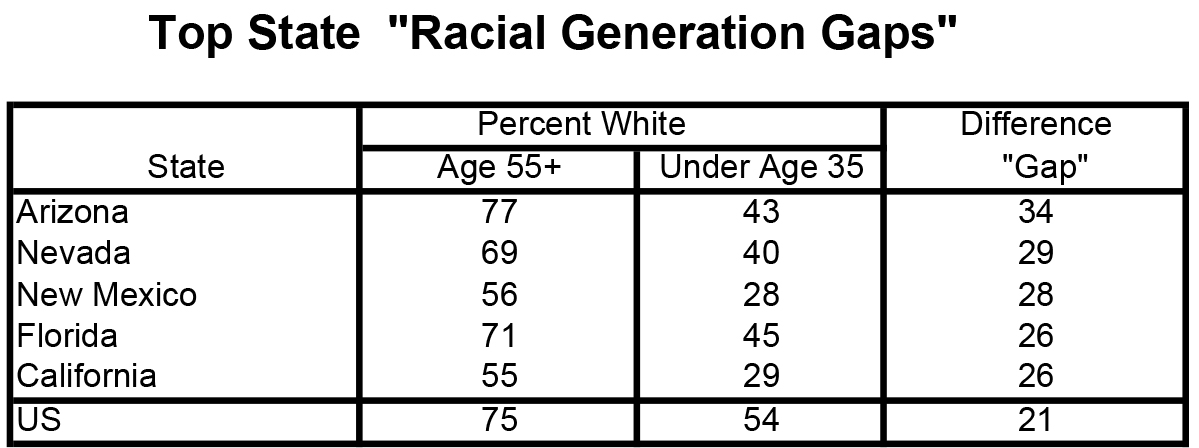
The rapid growth of minorities from the "lesser up" of the historic period structure is creating a racial generation gap betwixt the quondam and young that reflects the nation's irresolute demography. This gap is spilling over into national politics with older white Americans resonating differently than younger minorities on issues like government spending, affirmative action, and clearing.
The demographic fault line for the gap appears to lie between the population over age 55 and those nether age 35 (including millennials and mail-millennials). A short-hand measure is the deviation between the percent white amid these two populations (75 per centum vs. 54 percent for a "gap" of 21 pct, nationally). Moreover, the gap is specially loftier in states that that take received recent waves of new minority residents to counter more than established old whiter populations: Arizona leads all states with a gap of 33 percentage. (Not surprisingly the four states with highest gaps could exist competitive in this November's presidential election.)
The emerging political division associated with the racial generation gap represents just one surface area where members of the diverse millennial generation are on the front lines of change. While racial inequality exists within this generation (white millennials are amend educated and less susceptible to the forces of poverty than Hispanics and blacks), its members have embraced positive attitudes toward diversity more openly than their elders, and are responsible for much of the recent rising in interracial marriages.
As they move from young adulthood to middle age, millennials volition serve as a demographic span between older, whiter generations and subsequent, more various generations. Their power to digest, advocate, and go accustomed will be fundamental to the successful transition to a more racially diverse nation. Aye, millennials are worthy of attention. They are smart. They are artistic. They are passionate most many issues. But the nigh defining characteristic of the members of this unique generation, as the country evolves demographically, is their racial diversity.
gutierrezserow1958.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.brookings.edu/blog/the-avenue/2016/06/28/diversity-defines-the-millennial-generation/
0 Response to "Percentage of Baby Boomers That Voted Before Age 35"
Post a Comment